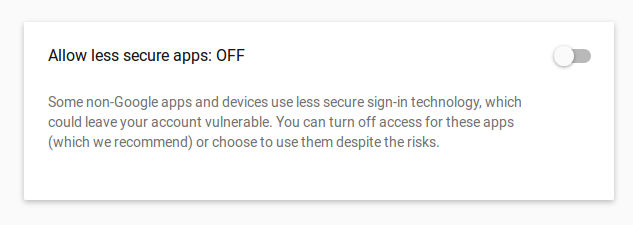
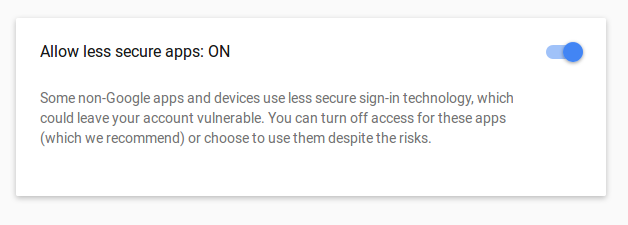
How To Send Email From Nodejs To Gmail
(Using NodeMailer)

In PHP, we can send e-mail using mail() function which internally uses/requires sendmail program (or equivalent program like postfix on Linux..)
See how to install and configure postfix to send e-mail from postfix
In the case of NodeJs, we can use NodeMailer NPM module to send emails from NodeJS. Here I'm going to show you how to send email from NodeJs to Gmail using NodeMailer NPM.
Step 1: Create/Initialize New Node Project
Create a folder and run npm init then create file named mail.js
Create New Folder For Node Project and Enter Into That Folder:
mkdir node-email && cd node-email
Now initialize project with npm init
npm init
The output of above command will look like following one..
shivaraj@shivaraj-A14RM0E:~/node-email$ npm init
This utility will walk you through creating a package.json file.
It only covers the most common items, and tries to guess sensible defaults.
See `npm help json` for definitive documentation on these fields
and exactly what they do.
Use `npm install <pkg> --save` afterwards to install a package and
save it as a dependency in the package.json file.
Press ^C at any time to quit.
name: (node-email)
version: (1.0.0)
description:
entry point: (index.js)
test command:
git repository:
keywords:
author:
license: (ISC)
About to write to /home/shivaraj/node-email/package.json:
{
"name": "node-email",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
Is this ok? (yes)
shivaraj@shivaraj-A14RM0E:~/node-email$
After completing above step you will see new file named package.json inside your node project directory. with following content..
{
"name": "node-email",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
Step 2: Now Install NodeMailer NPM
Now install NodeMailer NPM by running following command...
npm install nodemailer --save
You will see output similar to bellow one..
shivaraj@shivaraj-A14RM0E:~/node-email$ npm install nodemailer --save
node-email@1.0.0 /home/shivaraj/node-email
`-- nodemailer@2.7.0
+-- libmime@3.0.0
| +-- iconv-lite@0.4.15
| +-- libbase64@0.1.0
| `-- libqp@1.1.0
+-- mailcomposer@4.0.0
| `-- buildmail@4.0.0
| +-- addressparser@1.0.1
| `-- punycode@2.0.1
+-- nodemailer-direct-transport@3.3.2
| `-- smtp-connection@2.12.0
| `-- httpntlm@1.6.1
| +-- httpreq@0.4.22
| `-- underscore@1.7.0
+-- nodemailer-shared@1.1.0
| `-- nodemailer-fetch@1.6.0
+-- nodemailer-smtp-pool@2.8.2
| `-- nodemailer-wellknown@0.1.10
+-- nodemailer-smtp-transport@2.7.2
`-- socks@1.1.9
+-- ip@1.1.4
`-- smart-buffer@1.0.11
npm WARN node-email@1.0.0 No description
npm WARN node-email@1.0.0 No repository field.
shivaraj@shivaraj-A14RM0E:~/node-email$
The package.json file will now look like this...
{
"name": "node-email",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"nodemailer": "^2.7.0"
}
}
Note the extra line added in package.json file...
"dependencies": {
"nodemailer": "^2.7.0"
}
The dependencies section indicates installed npm module name and version of that npm module...
So we are using NodeMailer version 2.7 for this tutorial...
Step 3: Create app.js
Now create app.js file inside our project folder which is going to host our code for sending email...
Step 4: Now start to write code to send email from nodejs..
Import NodeMailer module into your app.js file...
var nodemailer = require('nodemailer');
Now configure/initialize nodemailer by providing required data...
var transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({
host: 'smtp.gmail.com',
port: 465,
secure: true, //true --> will use ssl
auth: {
user: 'yourusername@gmail.com',
pass: 'your password'
}
});
Don't forget to replace user and pass fields with your email ID and password...
Now send mail with transporter.sendMail(mailOptions, callback)... where mailOptions is an object which holds from address, to address and subject of mail etc... the second one is a callback function...
var mailOptions = {
from: 'yourusername@gmail.com',
to: 'friend1@gmail.com, friend2@gmail.com',
subject: 'Hello',
text: 'Hello world',
html: '<b>Hello world </b>'
};
transporter.sendMail(mailOptions, function(error, info) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log('Message sent: ' + info.response);
}
transporter.close();
});
call transport.close() method to close the connection..
The final version of app.js file will look like below one..
var nodemailer = require('nodemailer');
var transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({
host: 'smtp.gmail.com',
port: 465,
secure: true,
auth: {
user: 'yourusername@gmail.com',
pass: 'your password'
}
});
var mailOptions = {
from: 'yourusername@gmail.com',
to: 'friend1@gmail.com, friend2@gmail.com',
subject: 'Hello',
text: 'Hello world',
html: '<b>Hello world </b>'
};
transporter.sendMail(mailOptions, function(error, info) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log('Message sent: ' + info.response);
}
transporter.close();
});
You can download full code sample from
github..
That's all... Now run the app.js file to send email to your friend1@gmail.com, friend2@gmail.com....
node app.js
If your email get delivered successfully then you will see output similar to one shown below..
shivaraj@shivaraj-A14RM0E:~/node-email$ node app.js
Message sent: 250 2.0.0 OK 148xxxxxxx s5sxxxxxxxxxpgj.19 - gsmtp
shivaraj@shivaraj-A14RM0E:~/node-email$
That's it for now.. If you like don't forget to share it guys..
You can follow us on fb.com/opensourceinside and also subscribe our channel on Youtube..
Happy Coding !! ☻